Welcome to Jining Yizhan International Trade Co., Ltd
- January 06, 2025
Common Problems Encountered by General Small Excavators
I. Mechanical Components
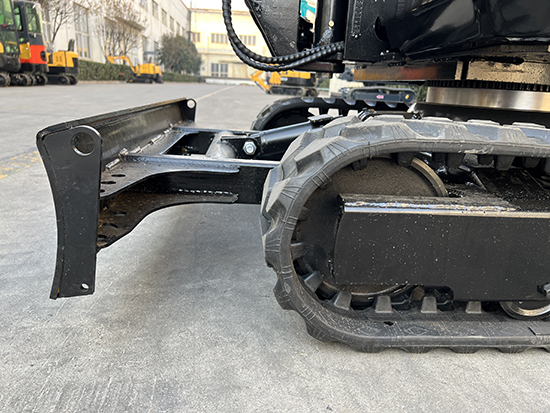
1. Track Issues
Track Loosening or Falling Off
Reasons: Operating on rough and uneven terrain for long periods, frequent turning, or improper adjustment of the track tension device can all cause the track to loosen. For example, when a small excavator is frequently working on construction waste piles at a building site, the track is subjected to uneven forces, making the pins connecting the track loose. If the track is too loose, it may fall off during operation.
Solutions: The track tension needs to be adjusted in a timely manner. The tension can be adjusted through the tension device (usually a grease cylinder) by adding or releasing grease to achieve the appropriate tension level. If the track has fallen off, first move the excavator to a flat area, reinstall the track using tools, and check and replace any damaged track pins and other components.
Track Wear
Reasons: The main reason is the harsh ground conditions at the work site. Working on surfaces such as gravel and sharp metal scraps can easily wear the rubber blocks and metal links of the track. Moreover, improper operation by the excavator operator, such as sudden acceleration and sharp turns while moving, can also exacerbate track wear.
Solutions: Regularly inspect the wear condition of the track. Slight wear can be tolerated with continuous observation. When the wear is severe and affects the walking safety and stability, the track components need to be replaced.
2. Bucket Tooth Damage
Reasons: When excavating hard foundations such as rocks and frozen soil, the bucket teeth bear huge impact and friction forces, making them prone to damage. Additionally, if the excavation angle is incorrect, for example, the bucket teeth are inserted into the material at an angle instead of vertically, the bucket teeth will be subjected to lateral forces and may break.
Solutions: Regularly check the wear and damage of the bucket teeth. Replace the damaged bucket teeth in a timely manner and choose high-quality bucket teeth that are suitable for the excavator model. At the same time, the operator should pay attention to the correct excavation method and try to make the bucket teeth penetrate the material vertically.
3. Slewing Bearing Failure
Reasons: The slewing bearing bears the weight of the upper structure and needs to rotate frequently. Long-term heavy-load operation or poor lubrication can lead to problems with the slewing bearing. For example, during the excavation process, if there are frequent large-scale rotations and lubricating grease is not added regularly, the friction between the raceway and rolling elements of the slewing bearing will increase, making it prone to wear, pitting, and other failures.
Solutions: Add lubricating grease to the slewing bearing according to the specified time intervals and requirements. Once abnormal noises or uneven rotation of the slewing bearing are detected, stop the machine immediately for inspection. If the wear is minor, the problem can be solved by adjusting the gap and re-lubricating. If the wear is severe, the slewing bearing may need to be replaced.
4. Leakage of the Working Device Hydraulic Cylinder
Reasons: The aging and damage of the sealing components of the hydraulic cylinder are the main reasons. After long-term use, the sealing components are affected by factors such as corrosion by hydraulic oil and intrusion of dust and impurities in the working environment, and lose their sealing performance. In addition, external impacts on the cylinder may also cause the cylinder body to crack and leak.
Solutions: Regularly inspect the appearance of the hydraulic cylinder for signs of oil leakage. If a small amount of leakage is found, first check the sealing components and replace the damaged ones. If the cylinder body is cracked, the cylinder needs to be replaced or the cylinder body repaired.

II. Hydraulic System
1. Excessive Hydraulic Oil Temperature
Reasons: Firstly, the overload of the hydraulic system. For example, long-term high-load excavation operations cause components such as the hydraulic pump and hydraulic motor to work under high pressure for a long time, generating a large amount of heat. Secondly, the hydraulic oil radiator is blocked. When the excavator works in a dusty environment, the radiator fins are covered with dust, affecting the heat dissipation effect.
Solutions: If it is due to overload, appropriately reduce the working intensity and give the excavator some rest intervals. For the blocked radiator, regularly clean the radiator. Compressed air or a high-pressure water gun (note that the pressure should not be too high to avoid damaging the radiator) can be used to remove dust and debris.
2. Insufficient Hydraulic System Pressure
Reasons: One of the common reasons is the failure of the hydraulic pump. For example, the internal parts of the hydraulic pump are worn, resulting in a reduced displacement of the pump and an inability to provide sufficient pressure. It is also possible that the safety valve in the hydraulic system malfunctions, opening prematurely or failing to close properly, preventing the system pressure from reaching the normal working pressure.
Solutions: Use a pressure gauge to check the pressure of the hydraulic system. If it is a hydraulic pump failure, the hydraulic pump needs to be repaired or replaced. For the safety valve failure, check whether the valve core of the safety valve is stuck by impurities and whether the spring is ineffective. Clean or replace the damaged components.
3. Hydraulic Oil Leakage
Reasons: In addition to the leakage of the hydraulic cylinder mentioned above, loose joints of the hydraulic pipelines and damaged sealing components are also the reasons for hydraulic oil leakage. During the operation of the excavator, due to factors such as vibration, the pipeline joints may gradually loosen, or the sealing components may age and wear.
Solutions: Regularly inspect the joints and sealing components of the hydraulic pipelines. For loose joints, retighten them and check the sealing condition. Replace the damaged sealing components. For the leaking pipelines, if they are severely damaged, new pipelines need to be replaced.
III. Electrical System
1. Battery Failure
Reasons: If the excavator is not used for a long time without proper battery maintenance, the battery will discharge itself and run out of power. In addition, operating in high or low temperature environments can also affect the battery performance. For example, in cold weather, the viscosity of the battery electrolyte increases, and the chemical reaction rate slows down, resulting in a decrease in battery capacity.
Solutions: If the battery is out of power, charge it using a dedicated charger. When the excavator is not used for a long time, charge the battery regularly. In extreme temperature environments, appropriate measures can be taken. For example, add a warming device to the battery in cold weather and pay attention to ventilation and heat dissipation in hot weather.
2. Electrical Wiring Faults
Reasons: The working environment of the excavator is harsh, and the electrical wiring is easily affected by factors such as vibration, humidity, dust, and oil. For example, the insulation layer of the wire may be corroded by oil, leading to a short circuit. Loose wiring connections can prevent electrical equipment from working properly.
Solutions: Regularly inspect the electrical wiring to check for any damage, aging, or loose connections. For damaged wires, replace them with new ones or wrap them with insulating tape. For loose connections, retighten them and take appropriate waterproof and dustproof measures.
Product Categories
Popular Products
Copyright ©2024 All Rights Reserved by Jining Yizhan International Trade Co., Ltd






